Comparison of Motion Response Characteristics of Tension Leg Platform Structure Threestar and Fourstar
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35718/ismatech.v3i2.8481434Keywords:
Tension Leg Platform, Pontoon Configuration, Motion Response, Free Floating, Six Degree of FreedomAbstract
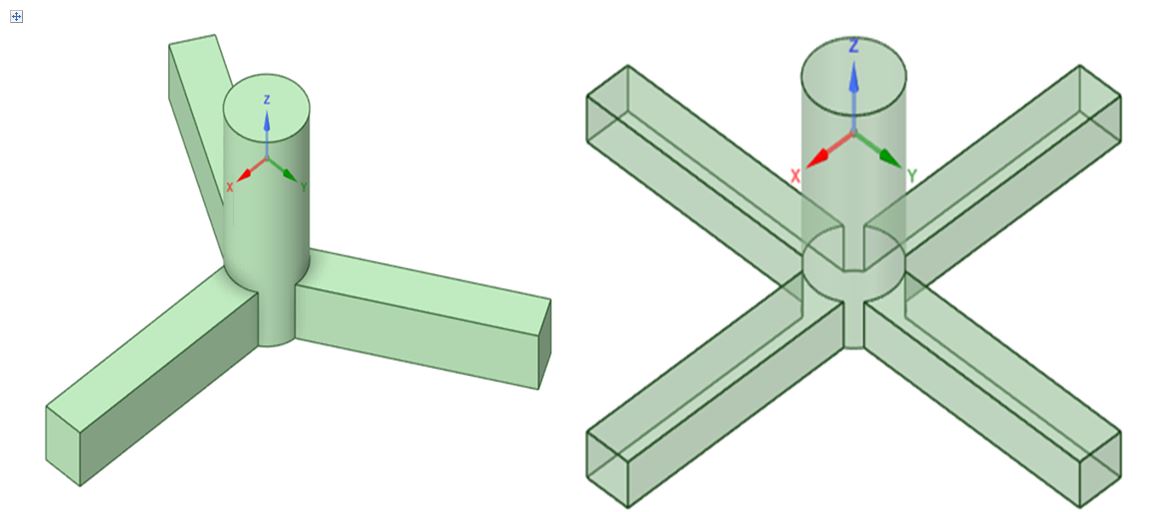
Tension Leg Platform (TLP) is a floating structure used for deep-sea oil and gas exploration with a tendon mooring system that maintains its stability. This study aims to compare the dynamic response of two TLP configurations, namely Threestar and Fourstar, during free-floating. Modeling is conducted numerically using ANSYS SpaceClaim and hydrodynamic simulation through ANSYS AQWA. The structural dimensions are modified from TLP A West Seno using displacement as validation. Environmental loading is based on wave, wind, and current data from the Makassar Strait waters. The simulation results show that the Threestar configuration has a higher Response Amplitude Operator (RAO) value in translational and rotational movements than Fourstar, except for heave movements where Fourstar is slightly more dominant. The difference in RAO values reflects the effect of the number and configuration of pontoons on structural stability. Fourstar, which is more symmetrical to the X and Y axes, shows a more stable response. In addition, TLP structures tend to show better performance in longer wave periods. Thus, the Fourstar structure is more recommended as it provides higher stability in challenging sea conditions.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Rafi Irsyad Syarief, Luh Putri Adnyani, Destyariani Liana Putri

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.



















